
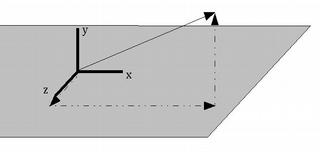
We normally describe a vector as a triplet of (X, Y, Z) values - (vx, vy, vz) represents a vector that points vx units in the direction of the X axis, vy units in the direction of the Y axis, and vz units in the direction of the Z axis.
e.g., (2, 0, 0) is a vector pointing in the direction of the X axis, 2 units long. (1, 1, 0) is a vector pointing at a 45 degree angle between the X and Y axes, 1.414 units long.
The magnitude of a vector (x,y,z) is its Euclidean length - the square root of vx2 + vy2 + vz2.