computer generated sensory support for as many of the senses as possible user centered 3D visuals interaction between real person and virtual world 3D sound haptics etc.

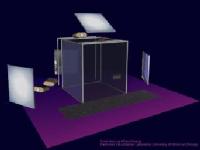
- First projected, immersive display developed at Electronic Visualization Laboratory, University of Illinois at Chicago
- VR theatre - rear projection - active stereo - 10' x10' x10' (3 x 3 x 3 m)
- electro-magnetic tracking for interaction
- surround sound
- motivation
- comfort - less encumbering
- comfort - less nausea
- community - a group can share environment
- result
- very spectacular, "wow" inspiring
- 100s of CAVEs and CAVE-alikes in world - mostly in research and industrial institutions
- drawbacks
- cost - in terms of both space and $$
- architectural footprint = 20' x 30' x 14' (6 x 9.1 x 4.25 m)
- SGI Reality Engine to generate graphics
- tracking systems
- projectors capable of maintaining active stereo - 96 Hz or better
- fragile equipment needing expert maintenance

- Smaller and lower cost projected systems developed commercially
- Immersadesk2 (at right), workbench, barco baron etc.
- lose completely immersive quality - more like looking through a window at the VR world - but an open window!
- Still relatively expensive because of:
- high price of high end graphics computers
- high price of generating active stereo & fragility of equipment

- Walls, reality centers, panorams, domes etc.
- Usually high end and high price
- Typically for applications that can sacrifice interactivity for a larger audience