

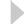
The Python function random.gauss(center, deviation) returns random numbers in a gaussian distribution.
The first argument (center) is the central number that the return
values will be clustered around. The second argument (deviation)
is the standard deviation of the distribution - this measures how broad the
bell curve is; roughly 2/3 of all returned values will be within +/- deviation
of the center value.
Example: a gaussian distribution lets you place objects randomly, but clustered about a center.
| Uniform | Gaussian |
|---|---|

| 
|